4. Alcohol-related causes of death are decreasing
Alcohol-related causes have been for several years among the most common causes of death for both men and women, and the figures are high for the whole population as well. Alcohol-related deaths include both alcohol-related diseases and accidental poisoning by alcohol.
Figure 7a. Age-standardised mortality from alcohol-related diseases and accidental poisoning by alcohol and total consumption of alcohol in 1969 to 2011
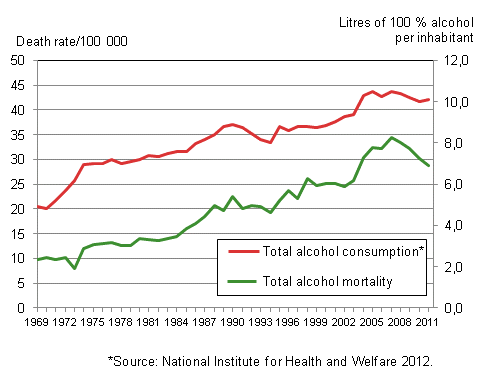
The most significant reason for high alcohol mortality is increased consumption of alcohol over the past decades. Changes in alcohol-related mortality follow fairly regularly the graph for total consumption of alcoholic beverages. As the alcohol tax was lowered in 2004, consumption of alcohol increased distinctly. At the same time, alcohol deaths increased considerably.
Figure 7b. Age-standardised mortality from alcohol-related diseases and accidental poisoning by alcohol in 1969 to 2011
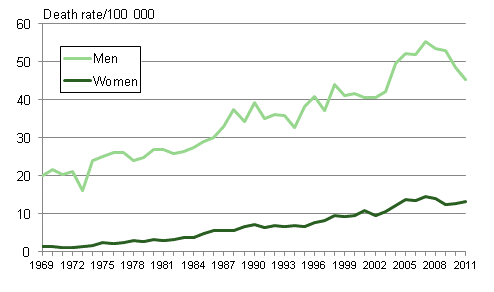
Men die from alcohol-related causes clearly more often than women do. Male mortality also follows more closely changes in total consumption of alcohol. However, female mortality has risen evenly along with men over several decades.
In 2011, 1,889 persons died from alcohol-related causes, 1,497 of whom from alcohol-related diseases and 392 from alcohol poisonings. Eighty per cent of those dying from alcohol poisonings were men. Most of those dying were at working age. The number of deaths from alcohol-related causes has been falling since 2009. The fall is mainly caused by decreasing alcohol deaths of men.
Alcohol can also be a contributing factor to death. The share of intoxication in accidents will be discussed in the following section.
Source: Causes of death, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Marja-Liisa Helminen 09 1734 3273, Airi Pajunen 09 1734 3605, kuolemansyyt@stat.fi
Director in charge: Jari Tarkoma
Updated 21.12.2012
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Causes of death [e-publication].
ISSN=1799-5078. 2011,
4. Alcohol-related causes of death are decreasing
. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 3.3.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/ksyyt/2011/ksyyt_2011_2012-12-21_kat_004_en.html

