Published: 29 September 2010
Production of electricity and industrial heat decreased in 2009
According to Statistics Finland's statistics on production of electricity and heat, production and total consumption of electricity fell by seven per cent in 2009. Electricity produced with hydro power and wood fuels declined by 26 and 17 per cent, respectively. At the same time, separate production of electricity with coal grew by 38 per cent. The need for and production of industrial heat decreased by 15 per cent as industrial output declined due to the economic downturn. Production of district heat, in turn, grew by six per cent, because the colder weather than last year increased the need for heating.
Production of electricity, district heat and industrial heat in 2000—2009
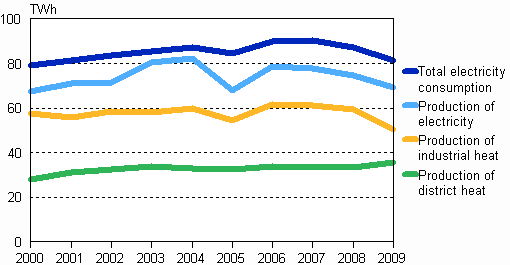
In 2009, total electricity consumption in Finland amounted to 81.3 terawatt hours (TWh) or billion kilowatt hours (kWh). Of this consumption, 85 per cent was covered by domestic production and the remaining 15 per cent by imported electricity. Electricity is imported to Finland from the Nordic countries, Russia and Estonia. Electricity is also exported from Finland to other Nordic countries and Estonia.
In 2009, the volume of electricity produced in Finland amounted to 69.2 TWh. The volume of electricity produced was seven per cent lower than one year previously. The production of district heat rose by six per cent and 15 per cent less heat was produced for industry than the year before. The production of district heat amounted to 35.5 TWh and that of industrial heat to 50.5 TWh.
The volume of electricity produced with renewable energy sources decreased by 22 per cent from the year before. The bad water situation in the Nordic countries reduced the domestic production of hydro power by 26 per cent. The decrease in renewable energy sources was also due to the industrial downturn, because the electricity produced with black liquor from the forest industry fell by 19 per cent and the electricity produced with other wood fuels went down by 14 per cent from the year before. The share of electricity produced with renewable energy sources in electricity production fell from its 36 per cent share to 30 per cent. In the production of renewable electricity hydro power accounts for 60 per cent, black liquor from the forest industry for 20 per cent and wood fuels for 17 per cent.
Electricity produced with coal went up by 26 per cent and the growth was biggest in the production of condensing power.
In all, 30 per cent of electricity was produced with renewable energy sources, 33 per cent with nuclear power and 30 per cent with fossil fuels. Eighteen per cent of electricity was produced with hydro power, 16 per cent with coal and 14 per cent with natural gas. Combined heat and power production remained as the most significant mode of electricity generation; it accounted for 36 per cent of all electricity produced in 2009.
Electricity and heat production by production mode in 2009
| Electricity, TWh | District heat, TWh | Industrial heat, TWh | Total fuels used, PJ 1) | |
| Separate production of electricity | ||||
| - Hydro power | 12,6 | - | - | - |
| - Wind power | 0,3 | - | - | - |
| - Nuclear power | 22,6 | - | - | - |
| - Condensing power 2) | 9,0 | - | - | 86,3 |
| - Total | 44,4 | - | - | 86,3 |
| Combined heat and power production | 24,8 | 26,6 | 40,2 | 399,2 |
| Separate heat production | - | 8,8 | 10,3 | 79,6 |
| Total production | 69,2 | 35,5 | 50,5 | 565,1 |
| Net imports of electricity | 12,1 | - | - | - |
| Total | 81,3 | 35,5 | 50,5 | 565,1 |
2) Condensing power includes condensing power plants, shares of condensing electricity of combined heat and power production plants, and peak gas turbines and similar separate electricity production plants.
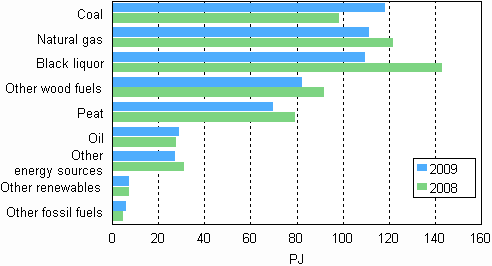
The use of fuels in the production of electricity and heat decreased by seven per cent in 2009.
Use of fuels in electricity and heat production in 2000—2009
Links:
Statistics Finland:
http://tilastokeskus.fi/keruu/ene/index_en.htmlFinnish Energy Industries:
http://www.energia.fi/en/statistics/rapidreportSource: Statistics on production of electricity and heat, Statistics Finland and Electricity statistics, Finnish Energy Industries
Inquiries: Minna Niininen 09 1734 3549, energia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Leena Storgårds
Publication in pdf-format (333.3 kB)
- Tables
-
Tables in databases
Pick the data you need into tables, view the data as graphs, or download the data for your use.
Appendix tables
- Appendix table 1. Electricity and heat production by production mode and fuel in 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix table 2. Fuel use in electricity and heat production, TJ (29.9.2010)
- Appendix table 3. Production and total consumption of electricity, GWh (29.9.2010)
- Appendix table 4. District heat production, GWh (29.9.2010)
- Appendix table 5. Industrial heat production, GWh (29.9.2010)
- Figures
-
- Appendix figure 1. Electricity production by energy sources 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 2. Electricity production by energy type 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 3. Electricity production by production mode 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 4. Electricity production with renewable energy sources 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 5. Electricity production with renewable energy sources 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 6. Heat production 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 7. District heat production by fuels 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 8. Industrial heat production by fuels 2000 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 9. Fuel use by production mode in electricity and heat production 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 10. Fuel use in electricity and heat production 2008 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 11. Fuel use in separate electricity production 2008 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 12. Fuel use in combined heat and power production 2008 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
- Appendix figure 13. Fuel use in separate heat production 2008 - 2009 (29.9.2010)
Updated 29.9.2010
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Production of electricity and heat [e-publication].
ISSN=1798-5099. 2009. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 23.2.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/salatuo/2009/salatuo_2009_2010-09-29_tie_001_en.html

