1. Sector-specific review on the data for the third quarter of 2013
1.1. Households' adjusted real income almost unchanged
The disposable income of households grew in the third quarter of 2013 by around EUR 0.7 billion, or by 2.5 per cent compared to the corresponding quarter in 2012. The key components of disposable income on the income side are wages and salaries received, entrepreneurial income and property income and social benefits received. The biggest expense items are taxes paid and social contributions.
Figure 1. Components of household sector adjusted disposable income
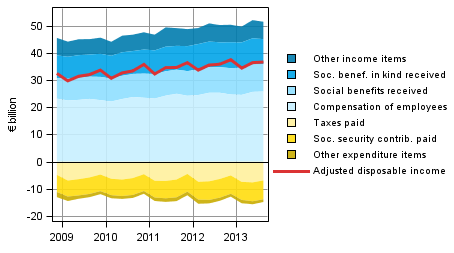
Compared to the figures one year ago, disposable income grew most due to a growth of good EUR 0.4 billion in wages and salaries and of close on EUR 0.6 billion in social benefits received. Entrepreneurial income also grew compared with the corresponding quarter of the previous year. On the expense side, income taxes paid grew by EUR 0.5 billion, while no significant changes took place in other expense items. Both interest income and expenses diminished from the corresponding quarter of one year before.
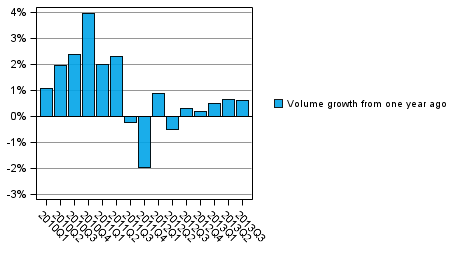
When received social benefits in kind are added to the disposable income of households, the household adjusted disposable income is derived, which is the indicator recommended by the OECD for measuring economic well-being. Social benefits in kind refer to education, health and social services produced by general government and non-profit institutions serving households. The real growth in adjusted disposable income has been modest over the past year, and in the third quarter the volume grew only by 0.6 per cent from the corresponding quarter of the previous year. The volume indicator describing the development of adjusted disposable income adjusted for price changes can be found in Appendix table 3 of this publication.
Figure 2. Volume development of households' adjusted disposable income
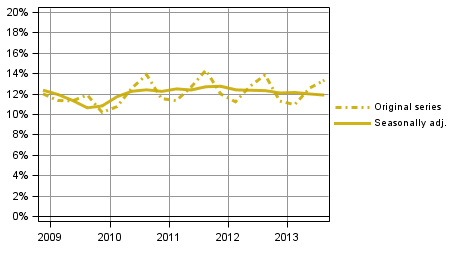
Households' seasonally adjusted saving rate was 2.9 per cent in the third quarter of 2013. In the previous quarter, it stood at 3.1 per cent. The saving rate is derived by deducting consumption expenditure from disposable income. The saving rate is negative if households' consumption expenditure is higher than their disposable income. Households' seasonally adjusted investment rate was 11.9 per cent of of disposable income in the third quarter of 2013, which was very close to the corresponding data of the previous quarter that stood at 12.0 per cent. Most of households' investments were investments in dwellings.
Figure 3. Households' saving rate
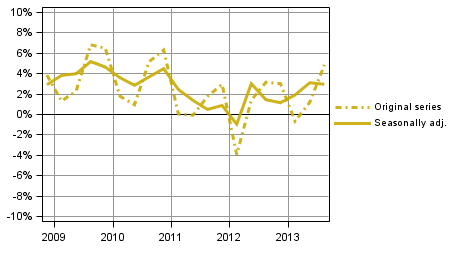
Figure 4. Households' investment rate
Wages and salaries paid by non-profit institutions serving households increased by two per cent compared with the quarter of one year ago.
In these statistics, the households sector only covers the actual households sector S14. Sector S15, non-profit institutions serving households is calculated and published separately. In Eurostat’s publication, the households sector also includes the data for sector S15. Another difference to Eurostat's publication is in how consumption of fixed capital is taken into account: Eurostat publishes investment and saving rates as gross figures, i.e. including consumption of fixed capital. Net data are used in these statistics, that is, when consumption of fixed capital is taken into account, saving and investment rates decrease.
1.2. Profits in the non-financial corporations sector increased slightly, investments on the decline
In the third quarter of 2013, the seasonally adjusted profit share of non-financial corporations, or the share of profits in value added, was 23.2 per cent. The profit share now rose after a break of almost one year. The increase is based on growth of value added while expenditure on wages and salaries remained unchanged.
Figure 5. Non-financial corporations' profit share
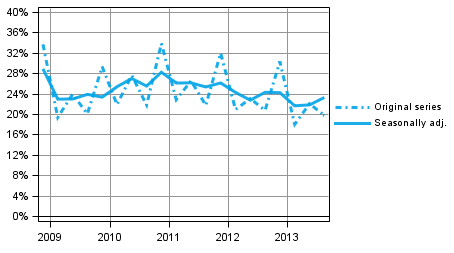
The investment rate of non-financial corporations, or the proportion of fixed capital investments in value added, continued to contract. In the third quarter of 2013, the investment rate was 21.2 per cent while the corresponding figure was 22.7 per cent in the previous quarter.
Figure 6. Non-financial corporations' investment rate
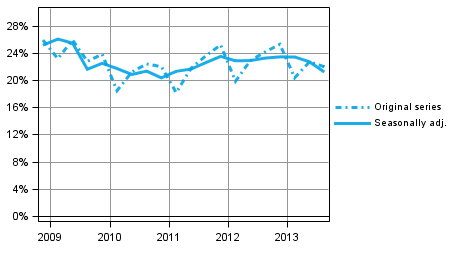
The general level of interest rates has remained low and is still strongly visible in the figures of the financial and insurance sector. The gross value added of the sector fell in the third quarter by eight per cent compared with the third quarter of last year, because intermediate consumption grew faster than output. Compensation of employees paid amounted to around three per cent less than in the year before. The operating surplus describing profits showed a fall of 18 per cent. Holding gains and losses generated through own securities trading are not visible in the value added and operating surplus; they describe the income that is generated from providing financial services to the public. In the third quarter, the property income in the sector was 25 per cent lower and property expenditure was 24 per cent lower than in the first quarter of last year.
1.3. The financial position of general government weakened from last year
General government unconsolidated total revenue grew by EUR 1.1 billion from the respective quarter of the previous year. Total expenditure in turn increased by EUR 1.4 billion. General government is comprised of central government, local government and social security funds. Unconsolidated total revenue and expenditure are figures in which flows between the general government sub-sectors have not been eliminated.
Figure 7. Components of general government sector net lending
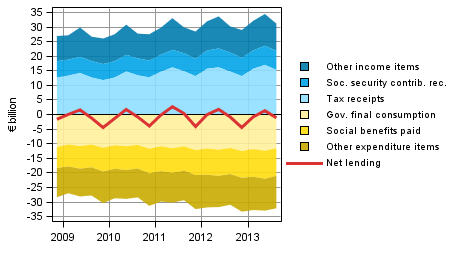
The general government deficit (net lending), which is formed as the difference between the total revenue and expenditure, increased by EUR 0.3 billion from one year ago. The financial position was particularly weakened by the increase in income transfers to other sectors and the decrease in the accumulation of taxes on products. Paid social contributions grew by roughly as much as social security contributions.
Of the sub-sectors, the financial position of local government improved, while the financial position of central government and social security funds weakened. More detailed statistics, where the sub-sectors are specified, are published in the quarterly sector accounts of general government: http://www.stat.fi/til/jtume/index_en.html
1.4. Foreign trade in balance in the third quarter
The essential items for the rest of the world sector are exports and imports of goods and services. Exports at current prices abroad from Finland amounted to EUR 19.2 billion in the third quarter of 2013. Exports of goods decreased by EUR 4.7 billion but that of services increased by EUR 10.2 billion from the corresponding quarter last year. Exports fell in particular for electronic products and grew for refined oil products.
Figure 8. Components of the balance of goods and services in foreign trade (from the perspective of the rest-of-the-world sector)
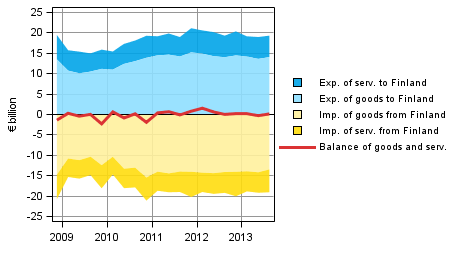
Note: Figures may differ from Bank of Finland's balance of payments figures due to differences in compilation schedules. This regards especially the latest quarters.
Imports at current prices to Finland were EUR 19.2 billion in the third quarter of 2013. Imports of goods increased by 0.4 per cent and those of services decreased by 1.6 per cent from one year ago. Imports fell most for metal ores and grew most for refined oil products and transport equipment.
Thus, the balance of goods and services was more or less in balance in the third quarter of 2013. One year ago, the balance showed a surplus of EUR 0.1 billion. The weakening in the balance of goods and services is compensated, for example, by the higher property income received from the rest of the world, which resulted in the current account staying at last year's level, showing a surplus of EUR 0.1 billion.
Figure 9. Components of the current account balance in foreign trade (from the perspective of the rest of the world sector)
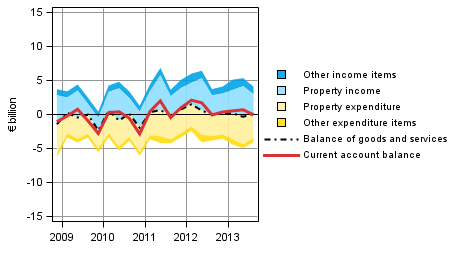
Note: Figures may differ from Bank of Finland's balance of payments figures due to differences in compilation schedules. This regards especially the latest quarters.
1.5. Data and methods used
The quarterly data become revised as source data are updated. The biggest revision will take place for the latest two to three years, because then the data in the annual accounts are still preliminary. Examined by quarter, the biggest revisions take place in the release for the second quarter at the turn of September and October, when the most recent data of annual national accounts from July are available for the first time. The data in the publication are based on the data sources available by 12 December 2013. The data for 1999 to 2012 correspond with the annual sector accounts of the national accounts, although concerning the year 2012, the updating of source data causes differences to the previous annual accounts data release.
The savings rate, profit share and investment rate in the quarterly publication of sector accounts are net amounts, i.e. consumption of fixed capital has been removed from the figures. The key indicators in these statistics were calculated as follows:
Households' saving rate = B8N / (B6N+D8R)
Households' investment rate = P51K / (B6N+D8R)
Profit share of non-financial corporations = B2N / B1NPH
Investment rate of non-financial corporations = P51K / B1NPH
The volume indicator, measuring the development of household adjusted disposable income, adjusted for price changes and its change percentages can be found in Appendix table 3 of this release. This volume index is calculated using the price data of the statistics on quarterly accounts, with which the components of adjusted disposable income are deflated. Household disposable income is deflated with the implicit price index of household consumption expenditure. Price data are also available for the consumption of non-profit institutions serving households. As a methodological shortcoming, general government individual consumption expenditure has to be deflated with the total general government consumption expenditure for lack of more accurate data. The volume time series was formed with the annual overlap method.
Source: Sector accounts, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Jesse Vuorinen 09 1734 3363, Katri Soinne 09 1734 2778, kansantalous.suhdanteet@stat.fi
Director in charge: Leena Storgårds
Updated 19.12.2013
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Quarterly sector accounts [e-publication].
ISSN=2243-4992. 3rd quarter 2013,
1. Sector-specific review on the data for the third quarter of 2013
. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 27.2.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/sekn/2013/03/sekn_2013_03_2013-12-19_kat_001_en.html

