4. Prevalence of types of families with children varies by area
4.1 Families of cohabiting couples are common in Åland
Family of a married couple is the most widespread type of family with children in all regions, although clear differences can also be seen. These arise from variations in the prevalence of families of cohabiting couples and single-parent families by region.
Åland and Lapland have the highest relative numbers of cohabiting couples. Central and South Ostrobothnia represent the other extreme. In Åland, 29 per cent and in Lapland 23 per cent of all families with underage children are families of cohabiting couples. The share of families of cohabiting couples is higher than the average for the whole country in 14 and lower than the average in six regions (Figure 7).
Figur 7. Proportions of cohabiting parents' families of all families with underage children by region in 2009
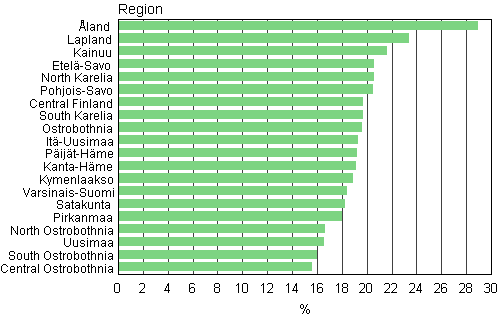
Examined by municipality, municipalities in Åland lead in the prevalence of cohabiting couples. Of the municipalities of Mainland Finland, Savukoski in the region of Lapland is at the top of the list with 33 per cent. In Luhanka 31 per cent of families with underage children are families of cohabiting couples. In Utsjoki, Kustavi and Enontekiö 30 per cent of families with children are families of cohabiting couples. In Mainland Finland, Luoto (6%) has the smallest relative proportions of cohabiting couples.
4.2 Fewest one-parent families with children in Ostrobothnia
There is also clear regional variation in the prevalence of one-parent families with children. In the figures by region, the Ostrobothnian regions differ from other regions in favour of the conventional family. The number of one-parent families is lowest there. The regions of Uusimaa and Päijät-Häme have the highest proportion (23%) of one-parent families with children. The share is high in Uusimaa because of Helsinki and in Päijät-Häme because of Lahti (Figure 8).
Figure 8. Proportions of single-parent families of all families with underage children by region in 2009
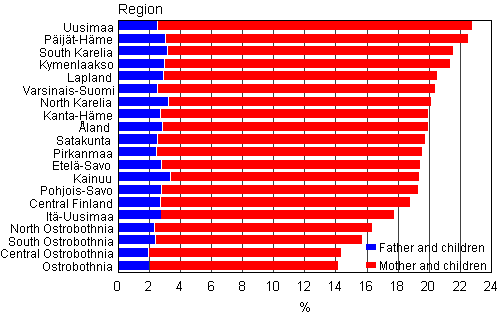
The regional variation in the proportion of one-parent families with children is due to the different proportions of families of the type mother and children. The proportion of families of the type father and children ranges from two to three per cent in all regions.
Examined by municipality, the relative numbers of one-parent families with underage children are highest in Sottunga (45%), Helsinki (29%), and Hartola and Maarianhamina (28%). Luoto (4%) and Yli-Ii (6%) have the lowest relative numbers of one-parent families with underage children in Mainland Finland.
Luoto could be regarded as the most conventional municipality in Finland in terms of family structure, as it has the smallest proportion of one-parent families with underage children and the largest respective proportion of married couples. After Merijärvi and Yli-Ii (2.86), as well as Sievi (2.85) it also has the fourth highest average number of 2.79 underage children living at home per family. The average for the whole country is 1.83.
The marital status of the majority of fathers and mothers of one-parent families with children is divorced. Only six per cent of the fathers and three per cent of the mothers are widowed. Dissolved cohabiting partnerships have increased the number of one-parent families with underage children with a mother or father who is unmarried. As many as 41 per cent of the mothers of families of the type mother and children are today unmarried, while the respective share among fathers of corresponding family type is 26 per cent (Table 3, Chapter 1).
Source: Population and Cause of Death Statistics, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Marjut Pietiläinen (09) 1734 2798, Timo Nikander (09) 1734 3250, vaesto.tilasto@stat.fi
Director in charge: Jari Tarkoma
Updated 30.11.2010
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Families [e-publication].
ISSN=1798-3231. Annual Review 2009,
4. Prevalence of types of families with children varies by area
. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 13.3.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/perh/2009/02/perh_2009_02_2010-11-30_kat_004_en.html

