Published: 18 November 2016
Warm weather decreased energy consumption in households in 2015
Corrected on 8 December 2016. The corrected items is indicated in red.
In 2015, electricity used in housing amounted to 61 terawatt hours (TWh). Consumption decreased by three per cent from the previous year. The record warm weather diminished the consumption of heating energy for spaces by five per cent. The energy consumption of household appliances went down by three per cent due to, for example, the decreased need to heat car interiors. The data are based on Statistics Finland's statistics on energy consumption in households.
Energy consumption in households 2010-2015
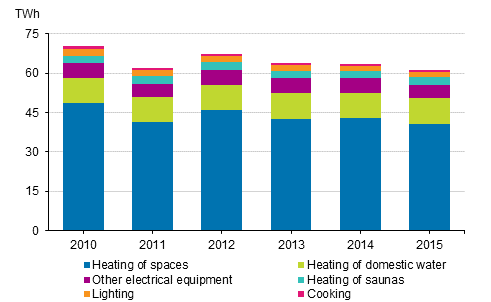
Sixty-six per cent of energy consumption in households concerned heating of residential buildings, 16 per cent heating of domestic water, and five per cent heating of saunas. In domestic appliances the share of lighting was three per cent, in cooking one per cent, and in other electrical appliances nine per cent of households’ energy consumption.
In 2015, electricity used on housing amounted to 21 TWh. Electricity consumption went down by two per cent from 2015. Forty-five per cent of electricity was used to heat indoor areas and 37 per cent to household appliances. The remaining share of electricity was used to heat domestic water and saunas. District heat and wood were the next most used energy sources in households. The energy consumption of households has decreased by 13 per cent in the first half of the decade. Housing accounted, on average, for 20 per cent of the final energy consumption.
Heating of residential buildings consumed 41 TWh of energy in 2015. Consumption decreased by five per cent from the previous year. The most common sources of energy for heating indoor spaces were district heat, wood and electricity, the share of which was 83 per cent of the energy consumption for heating indoor spaces. The next most common energy source was ambient energy, whose consumption is estimated to have grown by over 50 per cent since 2010. The consumption of other energy sources has declined simultaneously. Ambient energy refers to the energy extracted with heat pumps from the environment, the electricity use of heat pumps is in the statistics included in electricity consumption of heating. The cooling use of air heat pumps is currently included only in electricity consumption.
Outdoor temperature has an effect on the annual need for heating energy. Heating degree day is used to follow changes in that. According to the Finnish Meteorological Institute, there were four exceptionally warm years in the first half of the decade: 2011, 2013, 2014 and the record warm year 2015. In the warm years heating degree days decreased and thus the need for heating energy declined. Over the past five years the consumption of heating energy for heating indoor spaces has declined by 16 per cent.
Three TWh of wood and electricity was consumed to heat saunas in 2015. The energy consumption of heating domestic water was 10 TWh.
The energy consumption of household appliances, that is, cooking, lighting and other electrical equipment, was eight TWh in 2015. One per cent less energy was used on cooking, that is, using cookers and ovens, and two per cent less on lighting than in the year before. Use of energy-efficient lamps becoming more common is estimated to have decreased the electricity use of lighting by as much as 31 per cent since 2010.
The consumption of other electrical equipment fell by three per cent from the previous year. Other electrical equipment includes small appliances for cooking, refrigeration equipment, washing machines, tumble dryers, televisions and computers with their accessories, lifts, and car interior heating. Similarly as the heating energy of indoor spaces, the energy consumption of car interior heating went down due to the warm winter.
With respect to the consumption of heating energy in indoor spaces, domestic water and saunas, the statistics on energy consumption in households are based on Statistics Finland's calculation model where various sources were utilised. The energy consumption data of household appliances in terms of electricity consumption are based on the calculations of Adato Energia Oy. Part of the data have been estimated as the interval between the inquiries used as data sources has become longer.
The concepts of the statistics have been revised to correspond with the division of the new European Union's Regulation on energy statistics for households’ energy consumption. Based on the new division, the heating of indoor spaces, domestic water and saunas are reported separately.
Source: Energy consumption in households 2015, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Jonna Hakala 029 551 3419, energia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Ville Vertanen
Publication in pdf-format (250.5 kB)
- Tables
-
Tables in databases
Pick the data you need into tables, view the data as graphs, or download the data for your use.
Appendix tables
- Figures
Updated 18.11.2016
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Energy consumption in households [e-publication].
ISSN=2323-329X. 2015. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 28.2.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/asen/2015/asen_2015_2016-11-18_tie_001_en.html

