Published: 21 September 2012
Total energy consumption decreased by 5 per cent in January to June
According to Statistics Finland’s preliminary data, in the January to June period of 2012, total energy consumption amounted to around 705 PJ, which was five per cent less than in the corresponding period of 2011. The share of renewable energy of total energy consumption grew as the consumption of fossil fuels decreased and those of hydro and wind power, and wood fuels increased. Total electricity consumption amounted to 43.5 TWh, which was 2.4 per cent less than one year earlier. Electricity consumption decreased because nearly seven per cent less electricity was used in the forest industry. Carbon dioxide emissions from the production and use of energy diminished by nearly one-fifth.
Total energy consumption, PJ
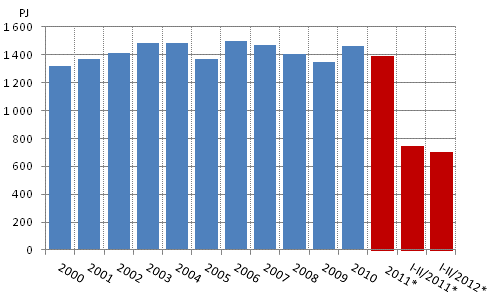
Almost one-quarter of Finland’s total energy consumption was covered by wood fuels. In January to June, total consumption of wood fuels increased by almost five per cent from twelve months back. Among individual energy sources, the largest reduction of 35 per cent (around 35 PJ) was seen in the consumption of coal, while the second largest reduction of 25 per cent (approx. 21 PJ) was recorded in the consumption of natural gas. The consumption of peat fell by 20 per cent. Increase in the consumption of hydro power amounted to 9 PJ, or nearly 43 per cent, due to better than average water reserves.
Total electricity consumption decreased by 2.4 per cent due to almost 10 per cent reduction in the forest industry’s electricity consumption and nearly five per cent reduction in the chemical industry’s electricity consumption. Domestic production of electricity decreased by 12 per cent. Combined heat and power production went down by 17 per cent. Combined heat and power production decreased by 16 per cent in industry’s combined power plants and by 19 per cent in district heating plants. The production of condensate power declined by 64 per cent, especially because domestic production of electricity was replaced with Nordic electricity imports. Net imports of electricity to Finland grew by 78 per cent due to increased imports of electricity from Sweden. For the first time, imports of electricity from Russia contracted by almost 60 per cent from the respective period of the previous year. Net imports of electricity amounted to 8.6 TWh in the first half of the year. Nearly 20 per cent of the electricity consumed in Finland was covered with imported electricity.
The value of diverse energy products imported into Finland in the January to June period was EUR 6.5 billion, which was six per cent higher than in the same period of 2011. Correspondingly, energy products were exported from Finland to the value of EUR 3.1 billion, which was 16 per cent more than during the respective period of the previous year. The energy products for which the biggest changes in import and export values were recorded were coal, medium distillates and electricity. In June, stocks of coal amounted to some 32 TWh, or over 30 per cent more than one year earlier. Respectively, stocks of peat were around 7.9 TWh, or almost one-quarter down at the end of June. Stocks of peat were considerably lower than last year due, among other things, to difficult production year.
Total energy consumption by source (TJ) and CO2 emissions (Mt)
| Energy source 4) | I-II/2012* | Annual change-%* | Percentage share of total energy consumption* |
| Oil | 156,864 | -5 | 22 |
| Coal 1) | 65,497 | -35 | 9 |
| Natural gas | 61,091 | -25 | 9 |
| Nuclear Energy 2) | 120,821 | 1 | 17 |
| Net Imports of Electricity 3) | 30,858 | 78 | 4 |
| Hydro and Wind Power 3) | 29,654 | 41 | 4 |
| Peat | 45,891 | -20 | 7 |
| Wood fuels | 171,049 | 5 | 24 |
| Others | 23,270 | 12 | 3 |
| TOTAL ENERGY CONSUMPTION | 704,994 | -5 | 100 |
| Bunkers | 15,176 | -13 | . |
| CO2 emissions from energy sector | 25 | -19 | . |
2) Conversion of electricity generation into fuel units: Nuclear power: 10.91 TJ/GWh (33% total efficiency)
3) Conversion of electricity generation into fuel units: Hydro power, wind power and net imports of electricity: 3.6 TJ/GWh (100%)
4) *Preliminary
Source: Energy supply and consumption. Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Pentti Wanhatalo 09 1734 2685, energia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Leena Storgårds
Publication in pdf-format (281.8 kB)
- Tables
-
Tables in databases
Pick the data you need into tables, view the data as graphs, or download the data for your use.
- Figures
-
- Appendix figure 1. Changes in GDP, Final energy consumption and electricity consumption (21.9.2012)
- Appendix figure 2. Carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels and peat use (21.9.2012)
- Appendix figure 3. Coal consumption (21.9.2012)
- Appendix figure 4. Consumption of natural gas (21.9.2012)
- Appendix figure 5. Peat consumption (21.9.2012)
- Appendix figure 6. Domestic oil deliveries (21.9.2012)
Updated 21.9.2012
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Energy supply and consumption [e-publication].
ISSN=1799-7976. 2nd quarter 2012. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 14.3.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/ehk/2012/02/ehk_2012_02_2012-09-21_tie_001_en.html

