This set of statistics has been discontinued.
New data are no longer produced from the statistics.
Published: 23 June 2010
Total energy consumption grew by 12 per cent
According to Statistics Finland's preliminary data, total energy consumption grew by 12 per cent year-on-year in the first quarter of the year. Consumption of electricity increased by 7 per cent. Energy consumption was put up by the cold weather in the early part of the year and by the recovered industrial production from the year before. Carbon dioxide emissions from energy production and use grew by nearly 20 per cent from twelve months ago. Emissions were put up by increased use of fossil fuels. Over 90 per cent more condensate power was produced with coal than one year earlier.
Total energy consumption, petajoule (1 petajoule = 1,000 terajoule)
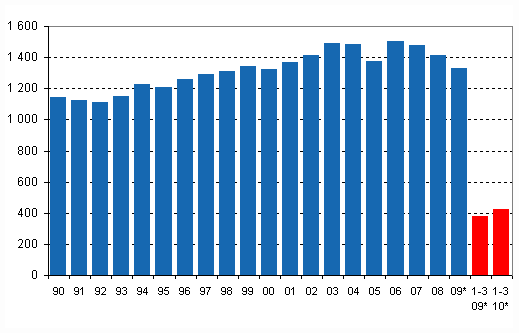
Emissions increased from the year before
The worsened water situation from the year before decreased the production of hydro power by 25 per cent. Among the other zero emission energy sources, the production of nuclear power was on level with the year before while the production of wind power decreased by just under one per cent. Along with the grown output of the forest industry the use of wood-based fuels increased by 7 per cent. However, this was by less than the growth of total consumption, so that their share of total consumption diminished from the previous year. The production of condensing power went up due to the diminished supply of hydro power and the cold weather in the early months of the year. The consumption of coal (includes here coal, coke and blast furnace and coke oven gas) and peat showed growth of nearly 40 per cent. The consumption of natural gas also went up by 18 per cent from the year before. Oil consumption showed 10 per cent growth. The increased use of fossil fuels and peat put carbon dioxide emissions up considerably. Carbon dioxide emissions were last at this level during the corresponding examination period of 2004.
Finland was net seller on the Nordic electricity market
Imports of electricity went up slightly but strong growth in electricity exports turned net imports of electricity to a decline. Throughout the past six months Finland has been a net seller on the Nordic electricity market. Electricity exports increased because of the poor water situation in the Nordic countries and maintenance shutdowns at nuclear power plants in Sweden. Despite the grown exports, over 8 per cent of Finland's electricity consumption was covered by net imports of electricity. Most of the imported electricity originated from Russia. In the early part of the year, the volume of electricity imports from Russia covered 12 per cent of total electricity consumption.
Fuel prices on the rise
From January to April fuel prices were going up. The prices of transport fuels rose by over 10 per cent and the price of light fuel oil by over 20 per cent from January 2009. Over the same time period the price of natural gas went up by 5 per cent. Cold weather in the early part of the year put the market price of electricity up strongly. The poor water situation in the Nordic countries and the paucity of the supply of nuclear power in Sweden caused strong peaks to the market price of electricity. At the most expensive trading hours the price of electricity in the Nordic electricity exchange Nord Pool reached as high as EUR 1,400 per megawatt hour. Towards the spring the price of electricity fell but still remained clearly above the previous year's level.
Sources: Energy supply, consumption and prices 2010, 1st quarter. Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Mr Anssi Vuorio +358 9 1734 2685, energia.tilastokeskus@stat.fi
Director in charge: Leena Storgårds
- Tables
-
Appendix tables
- Table 01. Total Energy Consumption by Source (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 02. Supplies and Total Consumption of Electricity (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 03. Energy Imports by Country of Origin January-March 2010 (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 04. Energy Exports by Recipient Country January-March 2010 (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 05. Consumer Prices of Liquid Fuels (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 06. Consumer Prices of Hard Coal, Natural Gas and Domestic Fuels in Heat Production (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 07. Price of Natural Gas by Type of Consumer (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 08. Price of Electricity by Type of Consumer (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 09. Price of District Heating by Type of Consumer (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 10. Excise Taxes, Value Added Taxes and Fiscal Charges and Fees Included in Consumer Prices of Some Energy Sources (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Table 11. Energy Taxes, Precautionary Stock Fees and Oil Pollution Fees (Excel) (23.6.2010)
- Figures
-
- Figure 01. Changes in GDP, Final energy consumption and electricity consumption 1995-, % (23.6.2010)
- Figure 02. Carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels and peat use 1990-, Mt (23.6.2010)
- Figure 03. Coal consumption 1993-, mill. t (23.6.2010)
- Figure 04. Consumption of natural gas 1993-, bn m3 (23.6.2010)
- Figure 05. Peat consumption 1993-, TWh (23.6.2010)
- Figure 06. Domestic oil deliveries 1993-, mill. t (23.6.2010)
- Figure 07. Import prices of oil 1997-, /t (23.6.2010)
- Figure 08. Consumer prices of principal oil products 1995-, c/l (23.6.2010)
- Figure 09. Fuel Prices in Heat Production 1995-, /MWh (23.6.2010)
- Figure 10. Fuel prices in electricity production 1995-, /MWh (23.6.2010)
- Figure 11. Price of electricity by type of consumer 1994-, c/kWh (23.6.2010)
- Figure 12. Average monthly spotprices at the Nord Pool power exchange 1998-, /MWh (23.6.2010)
Last updated 23.6.2010
Statistics:
Energy supply, consumption and prices [e-publication].
ISSN=1798-338X. 1st quarter 2010. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 23.2.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/ehkh/2010/01/ehkh_2010_01_2010-06-23_tie_001_en.html

