6. Effect of legislation and regulations on innovation activity
Now for the first time, enterprises were asked in more detail about the effects of legislation and regulations on innovation activity. The question covered legislation of several fields, that is, the answers show that for an enterprise some legislation may have an advancing effect on innovation activity and some other may be felt as a burden to development, depending on the situation.
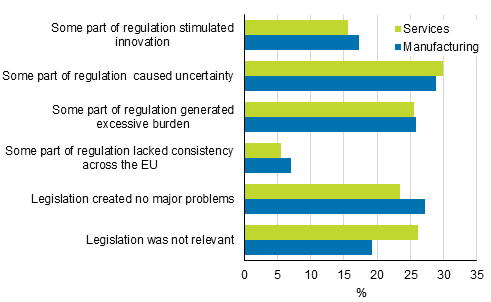
One-quarter of enterprises with innovation activity assessed that legislation did not cause significant problems to innovation activity in 2014 to 2016. In all, 16 per cent said that at least some legislation had stimulated the enterprise's innovation activity. Nearly every third, 30 per cent, assessed that some legislation had caused uncertainty in innovation activity and one quarter felt legislation had generated an excessive burden on the activity, that is, too regulatory legislation brought more burden to the enterprise than would have been necessary for attaining the objectives of legislation.
The mentioned legislation was not relevant at all for the innovation activity of around every fifth innovator.
Figure 20. Effect of legislation and regulations on innovation activity in manufacturing and services in 2014 to 2016, share of those with innovation activity
Of the mentioned legislation, environmental legislation was most commonly seen as stimulating innovation activity, and the second most commonly product safety and consumer protection legislation. The latter was also assessed most commonly as regulations generating an excessive burden and, of the mentioned regulations, it was felt most often to have lack of consistency across the EU. Four out of ten enterprises with innovation activity estimated for each of the mentioned legislation that the legislation did not cause significant problems. The results show that most uncertainty in innovation appears to be caused by data protection legislation and intellectual property rights.
The effects of legislation and regulations on innovation activity were generally seen very much alike in services and manufacturing. The share of enterprises that assessed that the mentioned legislation did not cause significant problems to innovation activity was larger in manufacturing than in services. In services, a larger share of enterprises thought that legislation was not relevant in the sense intended in the question.
The examination by size category showed that the said legislation is less relevant for the innovation activity of small enterprises than for large enterprises. Product safety and consumer protection legislation, and operational and worker safety legislation stimulate the innovation activity of the largest enterprises more often than any other legislation. Environmental legislation and intellectual property rights particularly stimulate the innovation activity of manufacturing enterprises and data protection legislation that of services.
Table 1. Effects of legislation or regulations on enterprises’ innovation activities by size category of personnel 2014-2016, share of enterprises with innovation activity
| Size category of personnel/ Legislation or regulation | Stimulated innovation | Created no major problems | Created uncertainty | Generated an excessive burden | Lacked consistency across the EU | Not relevant |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| 10–49 employees | ||||||
| Product safety / consumer protection | 4.9 | 36.3 | 6.3 | 10.2 | 2.0 | 43.2 |
| Operational and worker safety | 3.3 | 38.7 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 0.8 | 43.3 |
| Environmental | 4.4 | 38.7 | 5.5 | 7.8 | 1.7 | 44.0 |
| Intellectual property | 3.8 | 39.3 | 9.1 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 43.1 |
| Tax | 0.9 | 40.7 | 7.4 | 5.9 | 1.2 | 45.0 |
| Employment or social affairs | 1.5 | 38.1 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 0.8 | 48.1 |
| Data protection | 2.7 | 41.1 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 0.9 | 39.2 |
| Other | 1.7 | 38.0 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 1.8 | 48.3 |
| 50–249 employees | ||||||
| Product safety / consumer protection | 9.4 | 35.6 | 6.9 | 11.8 | 2.3 | 38.3 |
| Operational and worker safety | 7.7 | 46.5 | 3.3 | 8.6 | 1.4 | 34.3 |
| Environmental | 10.2 | 37.9 | 5.8 | 8.7 | 1.9 | 39.2 |
| Intellectual property | 3.8 | 45.8 | 9.2 | 3.9 | 0.4 | 38.6 |
| Tax | 1.0 | 43.4 | 7.2 | 4.4 | 1.4 | 44.7 |
| Employment or social affairs | 1.9 | 44.1 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 1.2 | 44.5 |
| Data protection | 4.4 | 42.6 | 13.8 | 8.5 | 1.1 | 32.5 |
| Other | 2.8 | 42.3 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 1.9 | 41.5 |
| 250– employees | ||||||
| Product safety / consumer protection | 16.2 | 39.8 | 10.7 | 12.7 | 6.8 | 25.9 |
| Operational and worker safety | 12.1 | 54.9 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 0.7 | 25.5 |
| Environmental | 23.5 | 39.6 | 9.9 | 8.2 | 3.1 | 24.9 |
| Intellectual property | 11.2 | 45.1 | 11.5 | 8.7 | 2.1 | 28.5 |
| Tax | 2.0 | 49.6 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 2.2 | 36.0 |
| Employment or social affairs | 2.0 | 55.5 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 1.4 | 36.9 |
| Data protection | 11.1 | 40.3 | 17.2 | 14.1 | 2.2 | 21.9 |
| Other | 6.5 | 43.9 | 8.1 | 6.8 | 5.3 | 35.1 |
Source: Innovation 2016, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Mervi Niemi 029 551 3263, Heidi Pirkola 029 551 3246, tiede.teknologia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Sami Saarikivi
Updated 12.4.2018
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Innovation [e-publication].
ISSN=1797-4399. 2016,
6. Effect of legislation and regulations on innovation activity
. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 12.3.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/inn/2016/inn_2016_2018-04-12_kat_006_en.html

