12. Protection of inventions and novelties and acquisition and transfer of intellectual property rights
Nearly every fifth enterprise surveyed, 18 per cent, had used some protection measures (patent application, utility model application, registration of industrial design right, registration of trademark, application for copyright or use of trade secret) in 2016 to 2018. The protection measures had been used by 28 per cent of enterprises with innovation activity, whose share of enterprises in the data was 62 per cent. In contrast, four per cent of enterprises with no innovation activity in 2016 to 2018 had carried out said protection measures.
The most commonly used protection measures were trademark registration, 18 per cent of those with innovation activity, and patenting, 12 per cent of innovators. A few per cent of those with innovation activity applied for a utility model, three per cent registered an industrial design right and nearly one per cent applied for copyright.
The use of the protection measures mentioned in the survey was more general in manufacturing than in service industries. In manufacturing the use of protection measures becomes significantly more common as enterprise size grows. Nine per cent of smaller manufacturing enterprise with innovation activity applied for a patent in 2016 to 2018, every fourth of medium-size enterprises and 60 per cent of the biggest enterprises. Respectively, the shares were two, seven and 25 per cent for registrations of industrial design right and 11, 27 and 46 per cent for trademark registrations.
Figure 17. Use of protection measures in total industry and services in 2016 to 2018, share of enterprises with innovation activity
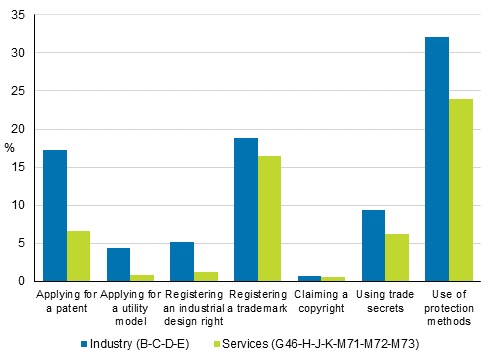
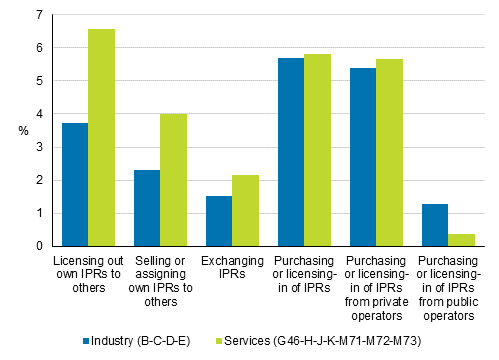
Five per cent of enterprises with innovation activity licensed out and three per cent sold or transferred their intellectual property rights (IPR) to others in 2016 to 2018. A couple of per cent of enterprises with innovation activity transferred (e.g. cross-licensing) intellectual property rights. Licensing, sale or other transfer of intellectual property rights, or their exchange, was most common among large enterprises, equally in manufacturing and service industries. For example, around every fifth enterprise with innovation activity in the biggest size category licensed out its intellectual property rights to others. For small and medium-size enterprises licensing and transfer of IPR took place somewhat more commonly in service enterprises than in manufacturing enterprises.
Around six per cent of those with innovation activity purchased or licenced-in patents or other intellectual property rights in 2016 to 2018. Intellectual property rights were most often acquired from the private sector. Acquisition of intellectual property rights was equally common in manufacturing and services.
Although the use of protection measures, such as patenting, was more general in manufacturing enterprises than in service enterprises, other measures connected to intellectual property rights were implemented in service industries more generally than in manufacturing.
For enterprises with no innovation activity in 2016 to 2018 measures related to intellectual property rights – licensing, sale, other transfer or acquisition – were of low occurrence.
Figure 18. Licensing, sale and other transfer of intellectual property rights (IPR) and acquisition in total industry and services in 2016 to 2018, share of enterprises with innovation activity
Further information about protection measures and acquisition and transfer of intellectual property rights
Protection and IPR measures and acquisition of knowledge and technology in enterprises by industry group and enterprise size categoryProtection and IPR measures and acquisition of knowledge and technology in enterprises by industry
Source: Innovation 2018, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Mervi Niemi 029 551 3263, Heidi Pirkola 029 551 3246, tiede.teknologia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Mari Yl�-Jarkko
Updated 23.4.2020
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Innovation [e-publication].
ISSN=1797-4399. 2018,
12. Protection of inventions and novelties and acquisition and transfer of intellectual property rights
. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 3.3.2026].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/inn/2018/inn_2018_2020-04-23_kat_014_en.html

